
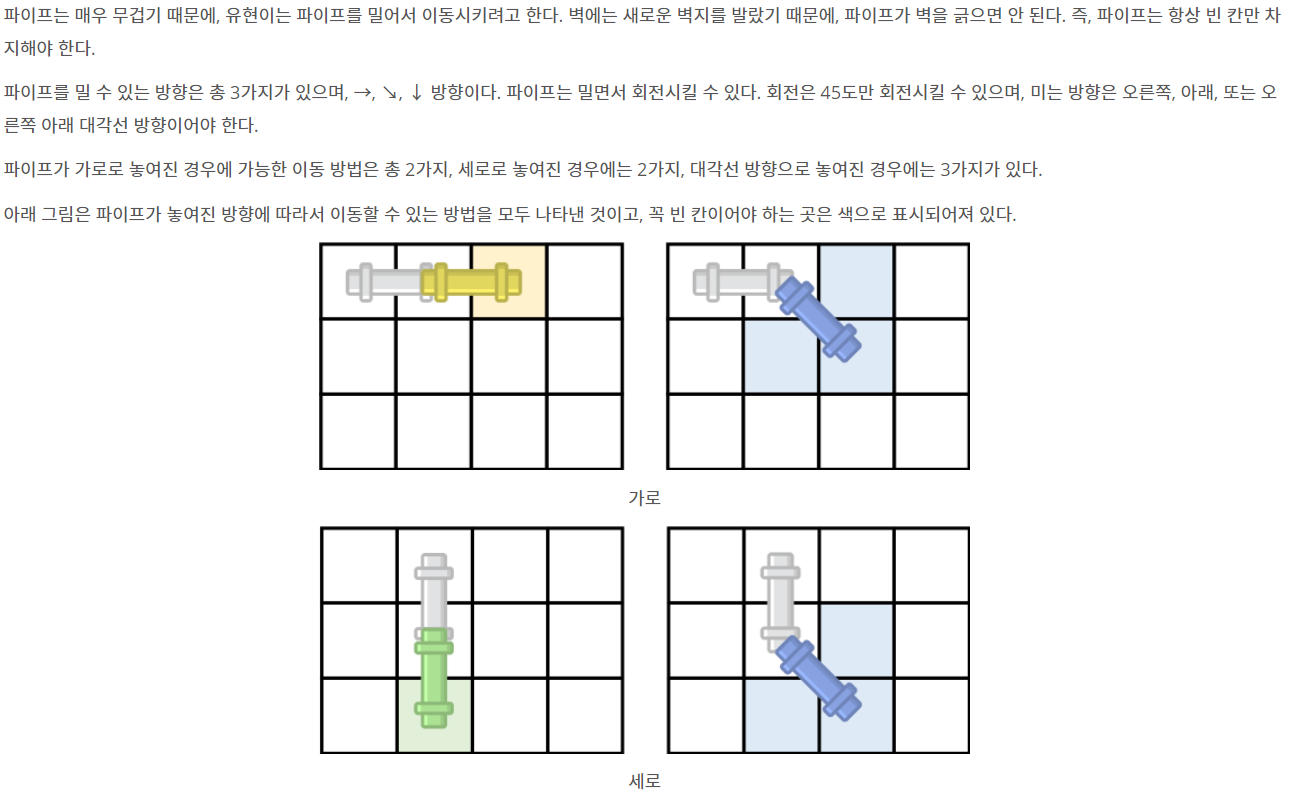
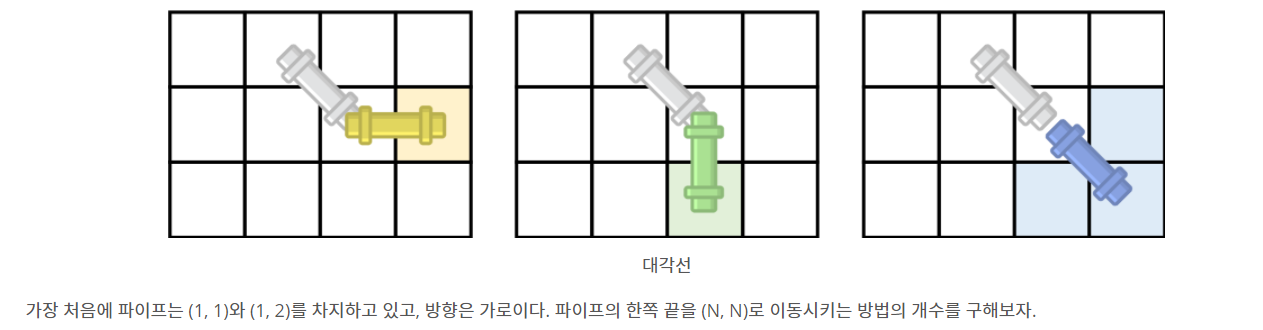
- 코드
정답 코드 : (0,1) 가로 일 때부터 시작해서 45도로만 움직일 수 있게 재귀문으로 반복해주면서 (N,N)까지 도달했을 때만 count++ 해줌.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int[][] array;
static int N;
static int count;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = null;
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
array = new int[N+1][N+1];
count = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
array[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
RecurPipe(1, 2, 0);
System.out.println(count);
}
private static void RecurPipe(int x, int y, int type) {
if(x == N && y == N && array[x][y] != 1) {
count++;
return;
}
// 가로
if(type == 0) {
// 오른쪽
if(check(x, y+1) && array[x][y+1] == 0)
RecurPipe(x, y+1, 0);
// 오른쪽 아래 대각선
if(check(x+1, y+1) && array[x+1][y+1] == 0 && array[x+1][y] == 0 && array[x][y+1] == 0)
RecurPipe(x+1, y+1, 2);
} else if(type == 1) { // 세로
// 밑
if(check(x+1, y) && array[x+1][y] == 0)
RecurPipe(x+1, y, 1);
// 오른쪽 아래 대각선
if(check(x+1, y+1) && array[x+1][y+1] == 0 && array[x+1][y] == 0 && array[x][y+1] == 0)
RecurPipe(x+1, y+1, 2);
} else if(type == 2) { // 대각
// 가로
if(check(x, y+1) && array[x][y+1] == 0)
RecurPipe(x, y+1, 0);
// 세로
if(check(x+1, y) && array[x+1][y] == 0)
RecurPipe(x+1,y, 1);
// 그대로 대각선
if(check(x+1, y+1) && array[x+1][y+1] == 0 && array[x+1][y] == 0 && array[x][y+1] == 0)
RecurPipe(x+1,y+1,2);
}
}
private static boolean check(int x, int y) {
return x>=1 && x<=N && y>=1 && y<=N;
}
}
다른 사람 코드 : 점화식을 이용해서도 풀 수 있다는 것을 보여준다.
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
class Main
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[][] map = new int[n][n];
long[][][] dp = new long[n][n][3];
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=0;j<n;++j) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
dp[0][1][0] = 1;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) {
for(int j=0;j<n;++j) {
//가로 => 대각선 + 가로
if(j+1 < n && map[i][j+1] == 0)
dp[i][j+1][0] += dp[i][j][1] + dp[i][j][0];
//대각선 => 대각선 + 가로 + 세로
if(j+1<n && i+1 < n && map[i+1][j] == 0 && map[i+1][j+1] == 0 && map[i][j+1] == 0)
dp[i+1][j+1][1] += dp[i][j][0] + dp[i][j][1] + dp[i][j][2];
//세로 => 대각선 + 세로
if(i+1<n && map[i+1][j] == 0)
dp[i+1][j][2] += dp[i][j][1] + dp[i][j][2];
}
}
System.out.println(dp[n-1][n-1][0] + dp[n-1][n-1][1] + dp[n-1][n-1][2]);
}
}
'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 백준 1013번 : Contact (0) | 2020.10.09 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 백준 11048번 : 이동하기 (0) | 2020.10.09 |
| [JAVA] 백준 11051번 : 이항 계수 2 (0) | 2020.10.06 |
| [JAVA] 백준 1991번 : 트리 순회 (0) | 2020.10.05 |
| [JAVA] 백준 12865번 : 평범한 배낭 (0) | 2020.10.05 |