11723번: 집합
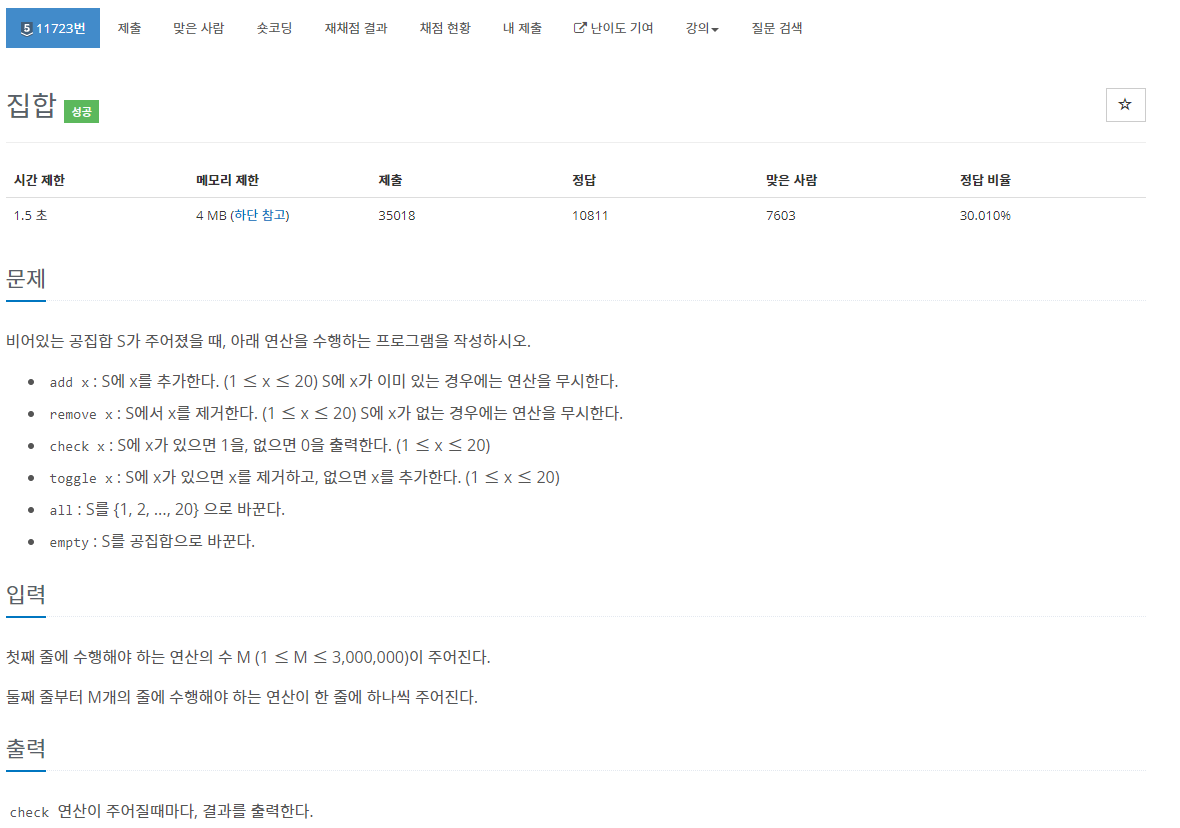
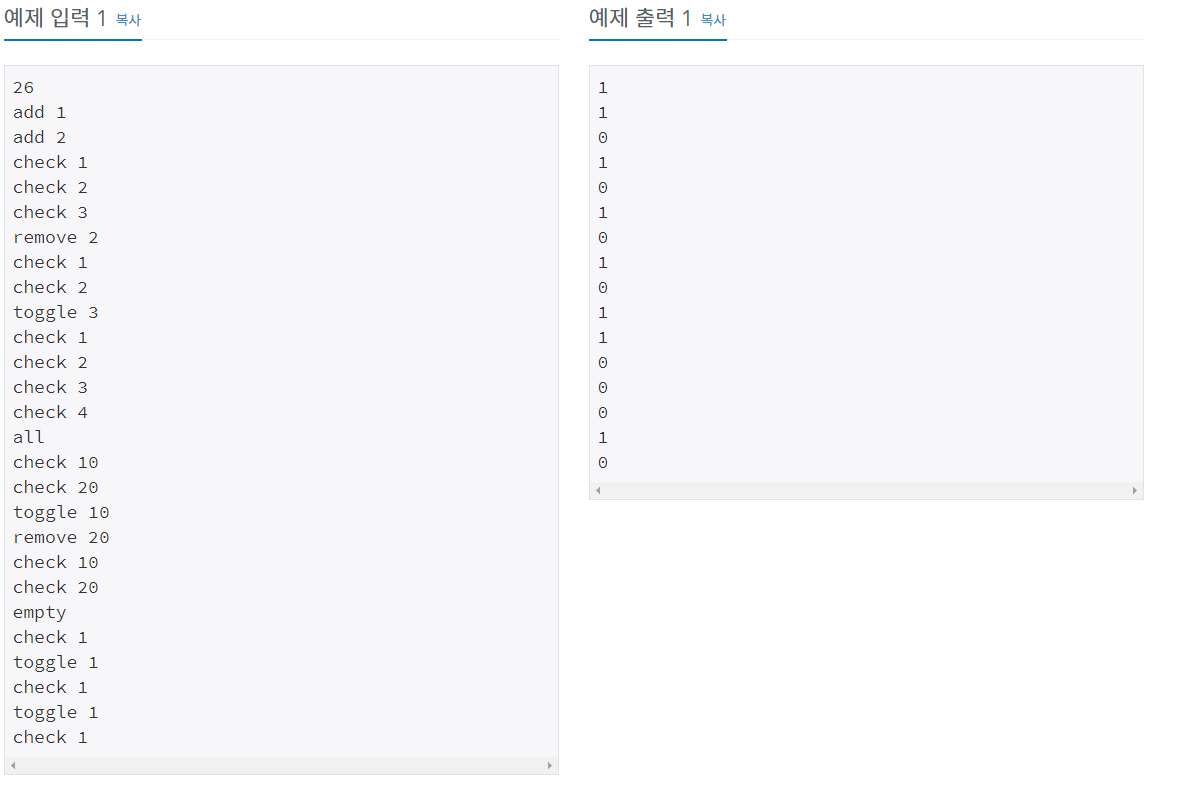
첫째 줄에 수행해야 하는 연산의 수 M (1 ≤ M ≤ 3,000,000)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 M개의 줄에 수행해야 하는 연산이 한 줄에 하나씩 주어진다.
www.acmicpc.net
- 풀이
HashSet을 사용해서 푼 문제이다. HashSet으로 하는 이유는 입력한 데이터 중 특정 값의 데이터가 있었는지 판단하기 쉽고, 추가하고, 지우기 간편하기 때문이다. 이러한 자료구조는 ArrayList도 있지만 Hashset이 더 빠르기 때문에 사용했다.
HashSet과 ArrayList의 차이점은 ArrayList는 넣은 순서대로 저장되지만 HashSet은 순서대로 저장되지 않는다.
이러한 차이점 때문에 HashSet이 더 빠르다고 보면된다.
참고) 원래는 비트마스킹으로 해결하라고 낸 문제이다.
- 코드
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
static int M;
static HashSet<Integer> set;
static StringBuilder sb;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SetData();
System.out.println(sb);
}
// 데이터
private static void SetData() throws Exception {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
M = in.nextInt();
set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++){
String[] s = in.nextLine().split(" ");
String command = s[0];
switch (command){
case "add" :
set.add(Integer.parseInt(s[1]));
break;
case "remove":
set.remove(Integer.parseInt(s[1]));
break;
case "check" :
if(set.contains(Integer.parseInt(s[1]))) sb.append("1\n");
else sb.append("0\n");
break;
case "toggle" :
if(set.contains(Integer.parseInt(s[1]))) set.remove(Integer.parseInt(s[1]));
else set.add(Integer.parseInt(s[1]));
break;
case "all" :
for(int num = 1; num<=20; num++){
set.add(num);
}
break;
case "empty" :
set.clear();
break;
}
}
}
//private static int SaveAnswer() {
//}
}
class InputReader {
private final InputStream stream;
private final byte[] buf = new byte[8192];
private int curChar, snumChars;
public InputReader(InputStream st) {
this.stream = st;
}
public int read() {
if (snumChars == -1)
throw new InputMismatchException();
if (curChar >= snumChars) {
curChar = 0;
try {
snumChars = stream.read(buf);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if (snumChars <= 0)
return -1;
}
return buf[curChar++];
}
public int nextInt() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c)) {
c = read();
}
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-') {
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
int res = 0;
do {
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
} while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public long nextLong() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c)) {
c = read();
}
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-') {
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
long res = 0;
do {
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
} while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public int[] nextIntArray(int n) {
int a[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = nextInt();
}
return a;
}
public String nextLine() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c))
c = read();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
do {
res.appendCodePoint(c);
c = read();
} while (!isEndOfLine(c));
return res.toString();
}
public boolean isSpaceChar(int c) {
return c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == '\t' || c == -1;
}
private boolean isEndOfLine(int c) {
return c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == -1;
}
}'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 14490번 : 백대열 (0) | 2021.08.05 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 11062번 : 카드 게임 (0) | 2021.08.04 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 13335번 : 트럭 (0) | 2021.08.04 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 18428번 : 감시 피하기 (0) | 2021.08.04 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 14569번 : 시간표 짜기 (0) | 2021.08.02 |