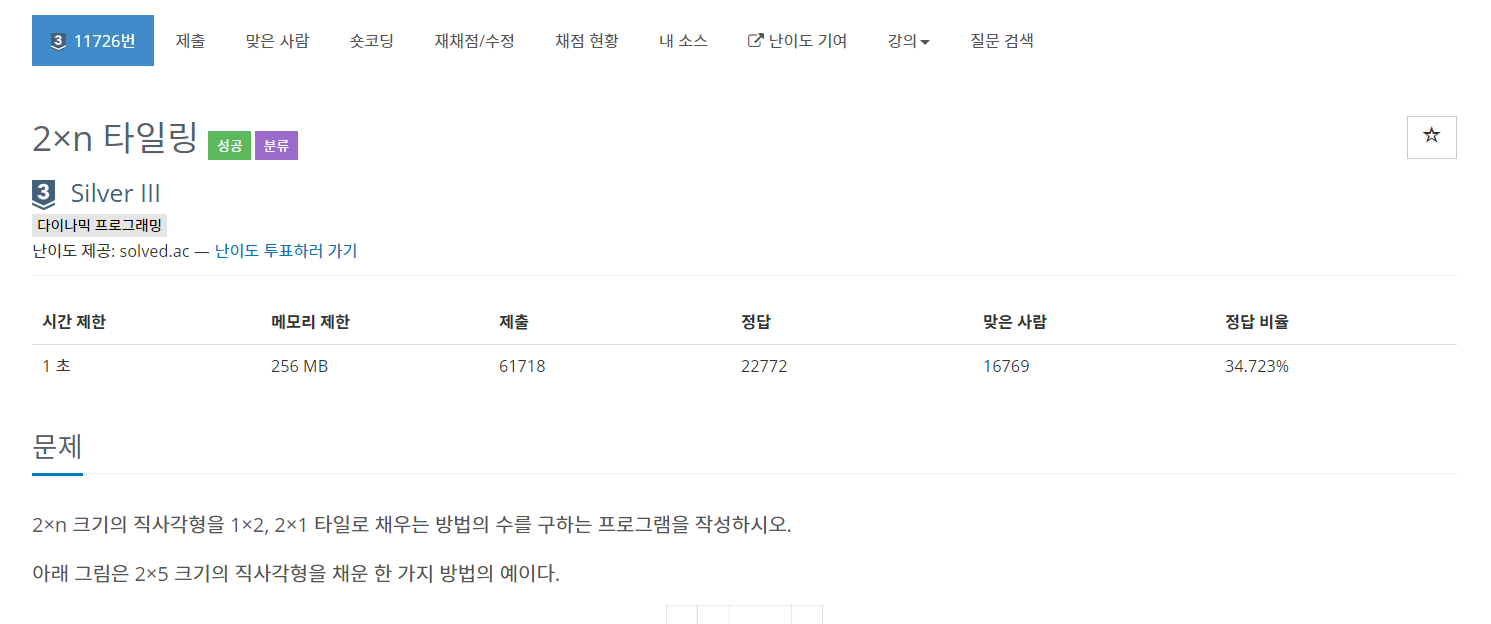
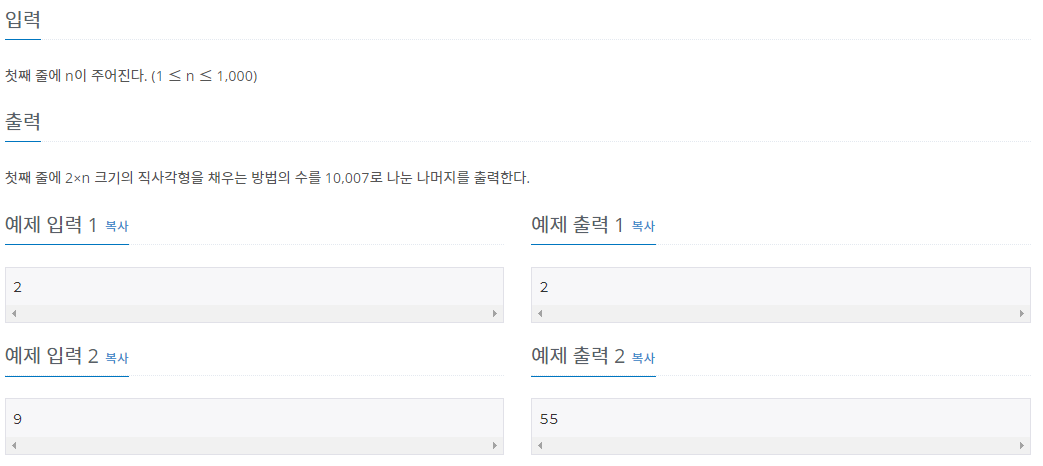
- 생각
몇개의 배열을 쫙 나열하면 구현할 수 있는 수준의 점화식이였다.
배열의 결과는
1 -> 2
2 -> 2
3 -> 3
4 -> 5
5 -> 8
느낌이 오는가?? 구하고 싶은 index에서 index-1, index-2의 값을 더 해주면 된다.
- 코드
- 점화식 : i번째 index의 값은 i-1와 i-2의 index의 값 합이라는 걸 토대로 구현하였다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int[] dp;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
dp = new int[1001];
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <1001 ; i ++) {
dp[i] = (dp[i-1] + dp[i-2]) % 10007;
}
System.out.println(dp[n]);
}
}
나중에 다시 풀어본 코드 : 배열에 접근할 때 런타임 에러에만 유의하면 될 것 같다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
private static int N;
private static int[] dp;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SetData();
System.out.println(dp[N]);
}
private static void SetData() throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
dp = new int[N + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
if(N == 1) return;
dp[2] = 2;
if(N == 2) return;
for (int i = 3; i <= N; i++) {
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]) % 10007;
}
}
}
'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 2212번 : 센서 (0) | 2021.01.07 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 14226번 : 이모티콘 (0) | 2021.01.07 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 11727번 : 2 x n 타일링 2 (0) | 2021.01.06 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 1463번 : 1로 만들기 (0) | 2021.01.05 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 17142번 : 연구소 3 (0) | 2021.01.05 |