2589번: 보물섬
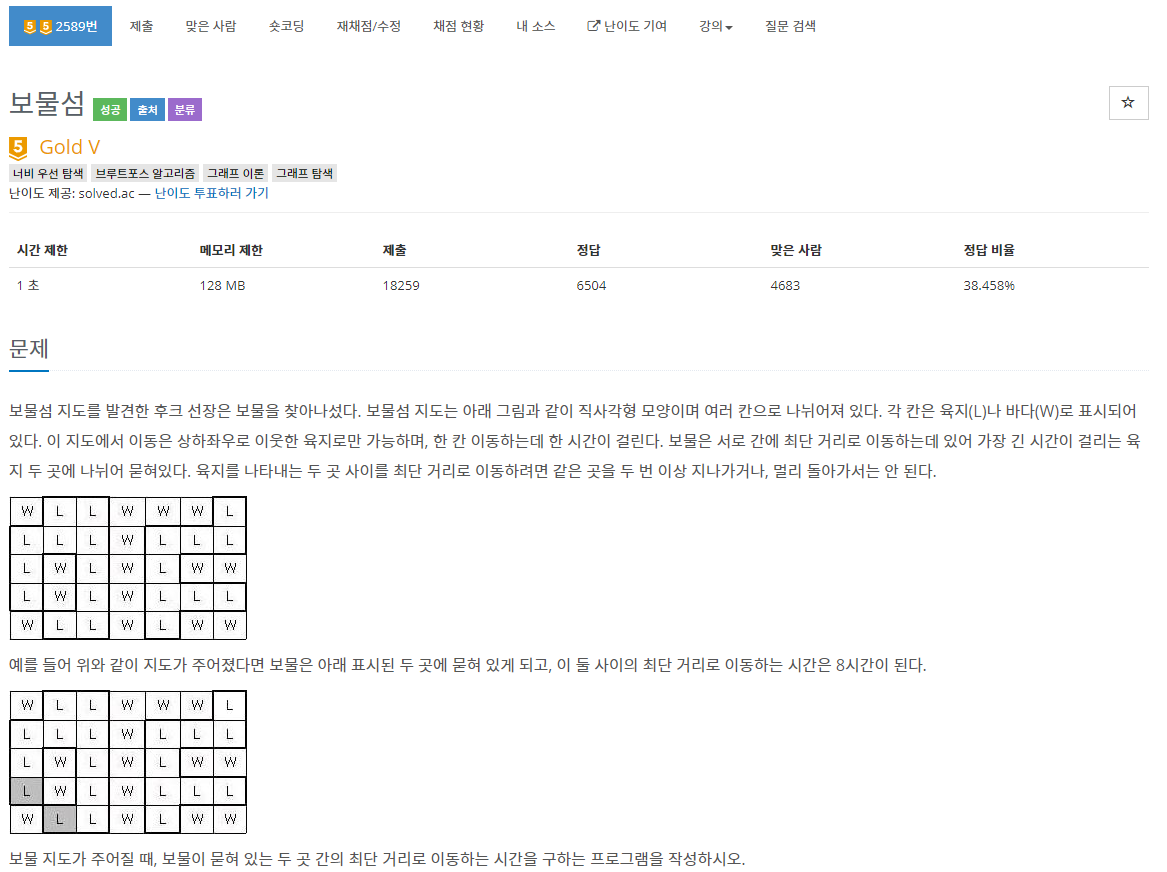
보물섬 지도를 발견한 후크 선장은 보물을 찾아나섰다. 보물섬 지도는 아래 그림과 같이 직사각형 모양이며 여러 칸으로 나뉘어져 있다. 각 칸은 육지(L)나 바다(W)로 표시되어 있다. 이 지도에서
www.acmicpc.net
- 생각
bfs 탐색
탐색을 하며 연결된 array 을 갈 때마다 큐의 사이즈를 재어주어 count 를 늘려줌
- 코드
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main{
static int M, N, count, answer;
static char[][] array;
static int[] x = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
static int[] y = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
static boolean[][] check;
static Queue<int[]> queue;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SetData();
System.out.println(answer - 1);
}
private static void SetData() throws Exception {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
M = in.nextInt();
N = in.nextInt();
array = new char[M][N];
check = new boolean[M][N];
queue = new LinkedList<>();
count = 0;
answer = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
String ss = in.nextLine();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
array[i][j] = ss.charAt(j);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (array[i][j] == 'L') {
bfs(i, j);
check = new boolean[M][N];
}
answer = Math.max(count, answer);
count = 0;
}
}
}
private static void bfs(int i, int j) {
queue.offer(new int[] { i, j });
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int len = queue.size();
count++;
for (int l = 0; l < len; l++) {
int location[] = queue.poll();
check[location[0]][location[1]] = true;
for (int direction = 0; direction < 4; direction++) {
int r = location[0] + x[direction];
int c = location[1] + y[direction];
if (r >= 0 && r < M && c >= 0 && c < N) {
if (!check[r][c] && array[r][c] == 'L') {
queue.offer(new int[] { r, c });
check[r][c] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
class InputReader {
private final InputStream stream;
private final byte[] buf = new byte[8192];
private int curChar, snumChars;
public InputReader(InputStream st) {
this.stream = st;
}
public int read() {
if (snumChars == -1)
throw new InputMismatchException();
if (curChar >= snumChars) {
curChar = 0;
try {
snumChars = stream.read(buf);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if (snumChars <= 0)
return -1;
}
return buf[curChar++];
}
public int nextInt() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c)) {
c = read();
}
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-') {
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
int res = 0;
do {
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
} while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public long nextLong() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c)) {
c = read();
}
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-') {
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
long res = 0;
do {
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
} while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public int[] nextIntArray(int n) {
int a[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = nextInt();
}
return a;
}
public String nextLine() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c))
c = read();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
do {
res.appendCodePoint(c);
c = read();
} while (!isEndOfLine(c));
return res.toString();
}
public boolean isSpaceChar(int c) {
return c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == '\t' || c == -1;
}
private boolean isEndOfLine(int c) {
return c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == -1;
}
}
메모리, 속도 측면에서 훨씬 좋은 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main{
static class Obj {
int y, x, cnt;
public Obj(int y, int x, int cnt) {
this.y = y;
this.x = x;
this.cnt = cnt;
}
}
static int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
static int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
static Queue<Obj> q;
private static int R;
private static int C;
private static int[][] map;
private static boolean[][] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
R = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
C = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
visited = new boolean[R][C];
map = new int[R][C];
q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
String s = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < C; j++) {
switch (s.charAt(j)) {
case 'W':
map[i][j] = 1;
break;
case 'L':
map[i][j] = 0;
break;
}
}
}
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 0 && !visited[i][j]) {
visited[i][j] = true;
q.add(new Obj(i,j,0));
checkMap(i, j);
int temp = findWay();
if (max < temp)
max = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static int findWay() {
int max = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Queue<Obj> q2 = new LinkedList<>();
Obj temp = q.poll();
q2.add(temp);
boolean[][] visited2 = new boolean[R][C];
while (!q2.isEmpty()) {
Obj cur = q2.poll();
visited2[cur.y][cur.x] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int ny = cur.y + dy[i];
int nx = cur.x + dx[i];
if (ny >= 0 && ny < R && nx >= 0 && nx < C && map[ny][nx] == 0 && !visited2[ny][nx]) {
visited2[ny][nx] = true;
q2.add(new Obj(ny, nx, (cur.cnt) + 1));
}
}
if (q2.isEmpty()) {
if (max < cur.cnt)
max = cur.cnt;
}
}
}
return max;
}
public static void checkMap(int y, int x) {
boolean check = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int ny = y + dy[i];
int nx = x + dx[i];
if (ny >= 0 && ny < R && nx >= 0 && nx < C && map[ny][nx] == 0 && !visited[ny][nx]) {
visited[ny][nx] = true;
check = true;
checkMap(ny, nx);
}
}
if (!check)
q.add(new Obj(y, x, 0));
}
}
'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 1083번 : 소트 (0) | 2021.02.05 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 2812번 : 크게 만들기 (0) | 2021.02.05 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 15918번 : 랭퍼든 수열쟁이야!! (0) | 2021.02.04 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 9576번 : 책 나눠주기 (0) | 2021.02.03 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 17406번 : 배열 돌리기 4 (0) | 2021.02.03 |