- 생각
T개 만큼의 숫자를 입력한 뒤 해당 수를 짝수 두개의 수로 나누어 떨어진 숫자 두개를 출력하면 된다. 단, 숫자의 차이는 최소여야 한다.
1. 에라토스테네스의 체를 통해 소수를 찾아 둔다.
2. 입력한수 / 2 한 값에서 부터 0까지 반복문을 돌면서 소수이고, 입력한수 - 반복문 도는 수를 했을 때 둘다 소수이면 출력한다.
- 코드
정답 코드 : 에라토스테네스의 체를 통해 소수를 찾고, 입력한수 / 2 값에서부터 반복문을 돌며 두개의 합이 입력한 수 이며 두 수 모두 소수이면서 값의 차이가 최소가 되는 값을 출력한다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
static int N;
static boolean[] check;
static StringBuilder sb;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SetData();
System.out.println(sb);
}
private static void SetData() throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
check = new boolean[10001];
getPrimeNumber();
sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int t=0; t < N; t++) {
int number = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = number/2; i > 0; i--) {
int index1 = i; // 소수 1
int index2 = number - i; // 소수 2
if(!check[index1] && !check[index2]) { // 둘 다 소수가 맞으
sb.append(index1 + " " + index2 + "\n");
break;
}
}
}
}
public static void getPrimeNumber() {
check[0] = check[1] = true;
for (int i = 2; i <= 10000; i++) {
if (check[i] == true) {
continue;
}
// 해당 수로 나누어 떨어지는 수는 소수이므로 true로 check
for (int j = i + i; j <= 10000; j+=i) {
check[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 백준 1292번 : 쉽게 푸는 문제 (0) | 2020.12.01 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 백준 1094번 : 막대기 (0) | 2020.12.01 |
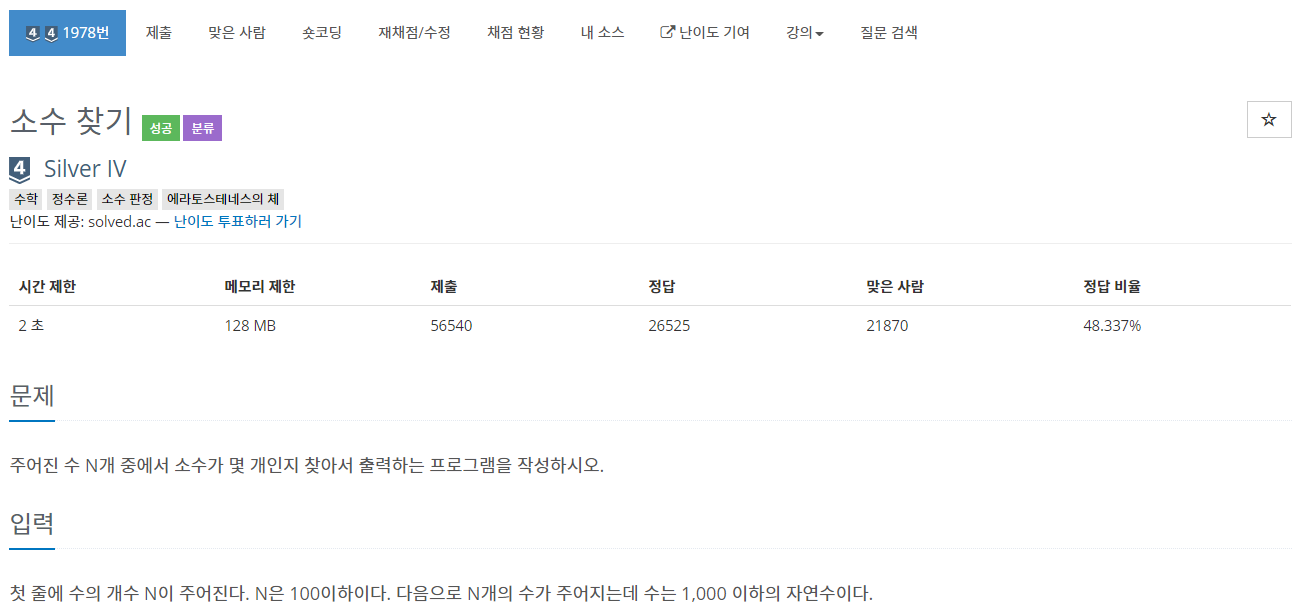
| [JAVA] 백준 1978번 : 소수 찾기 (0) | 2020.11.30 |
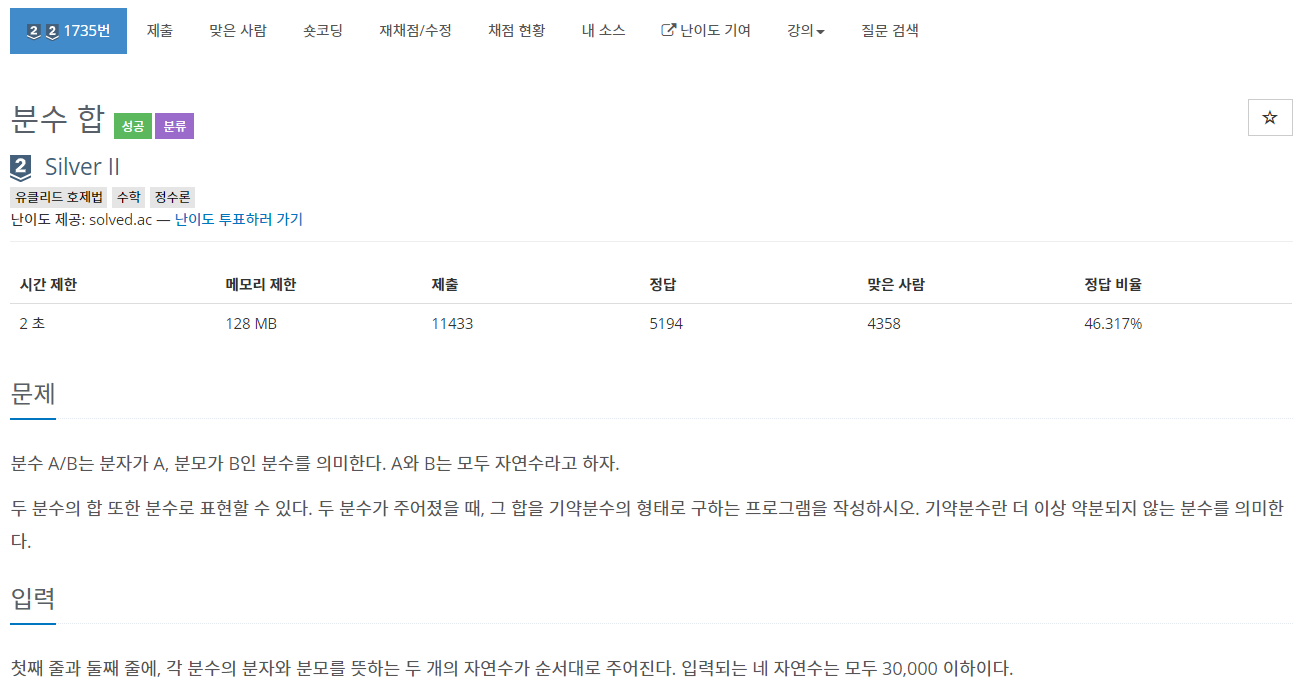
| [JAVA] 백준 1735번 : 분수 합 (0) | 2020.11.27 |
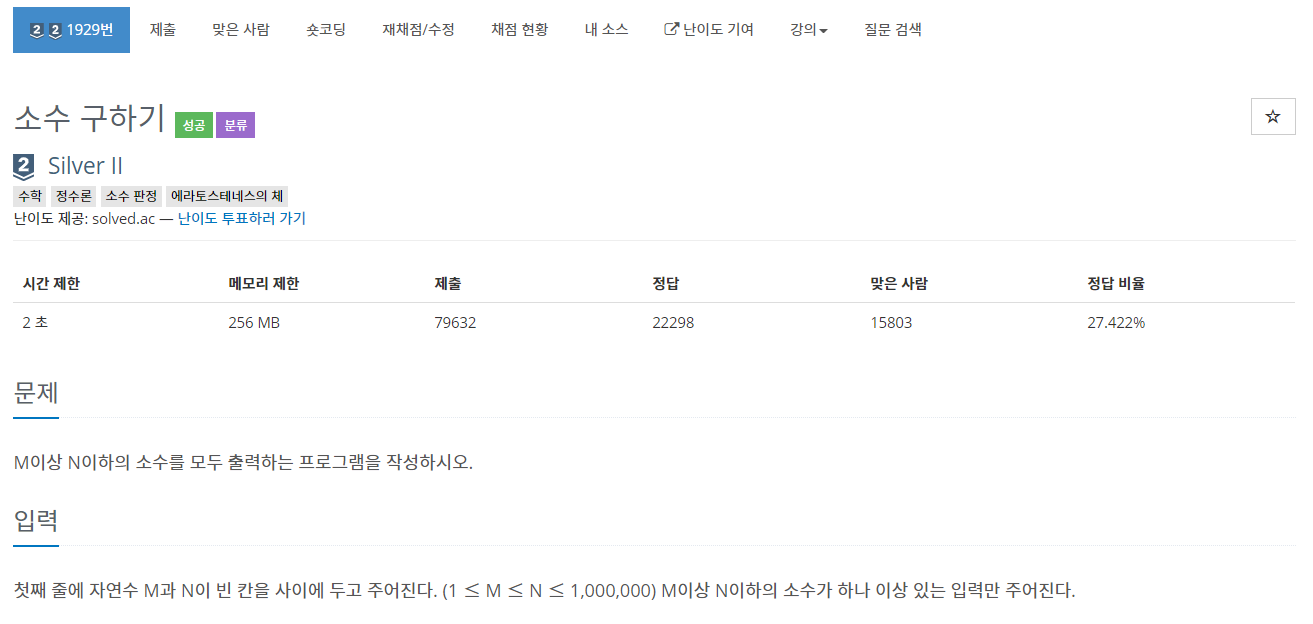
| [JAVA] 백준 1929번 : 소수 구하기 (0) | 2020.11.27 |