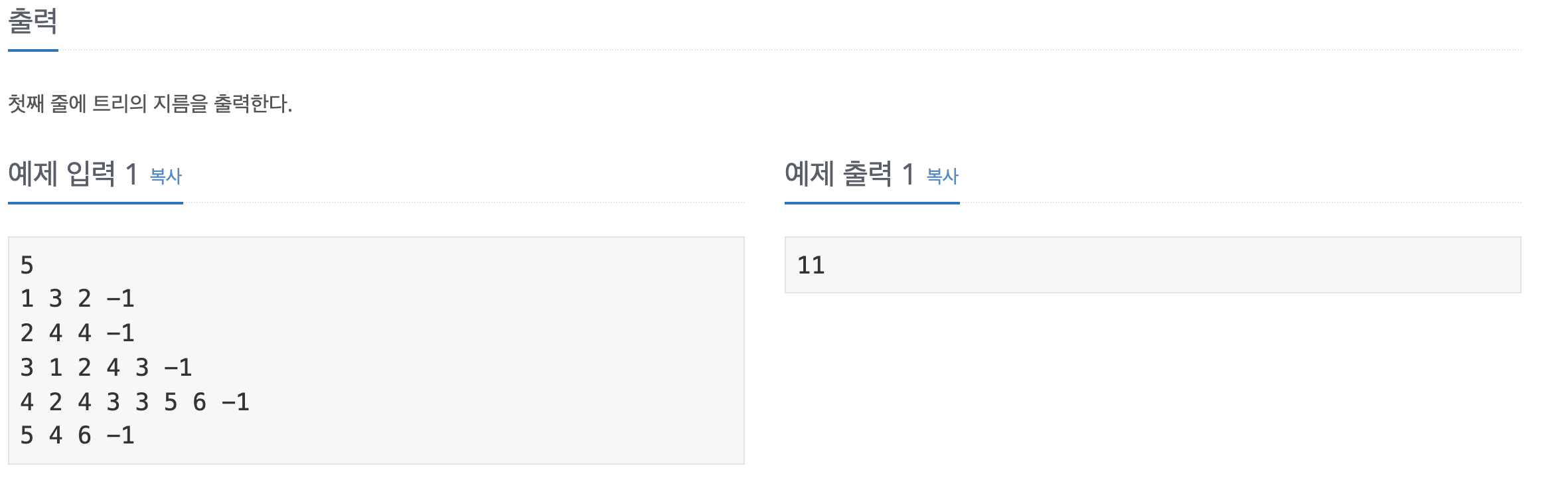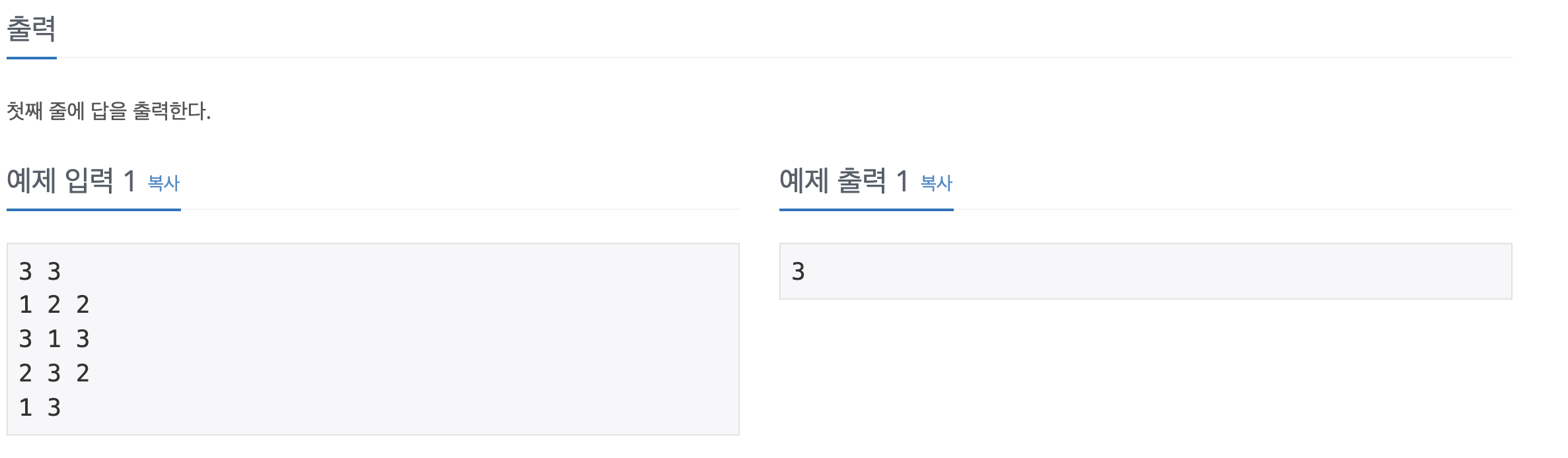
1238번: 파티
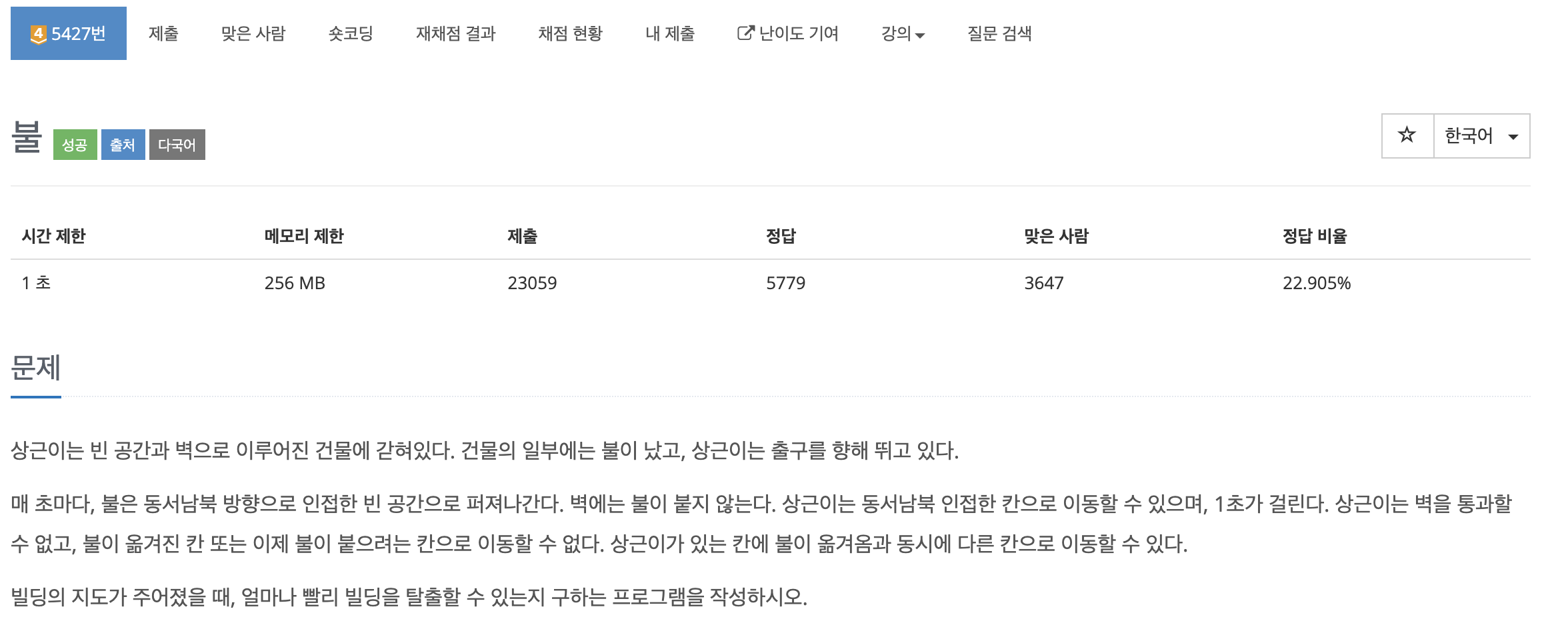
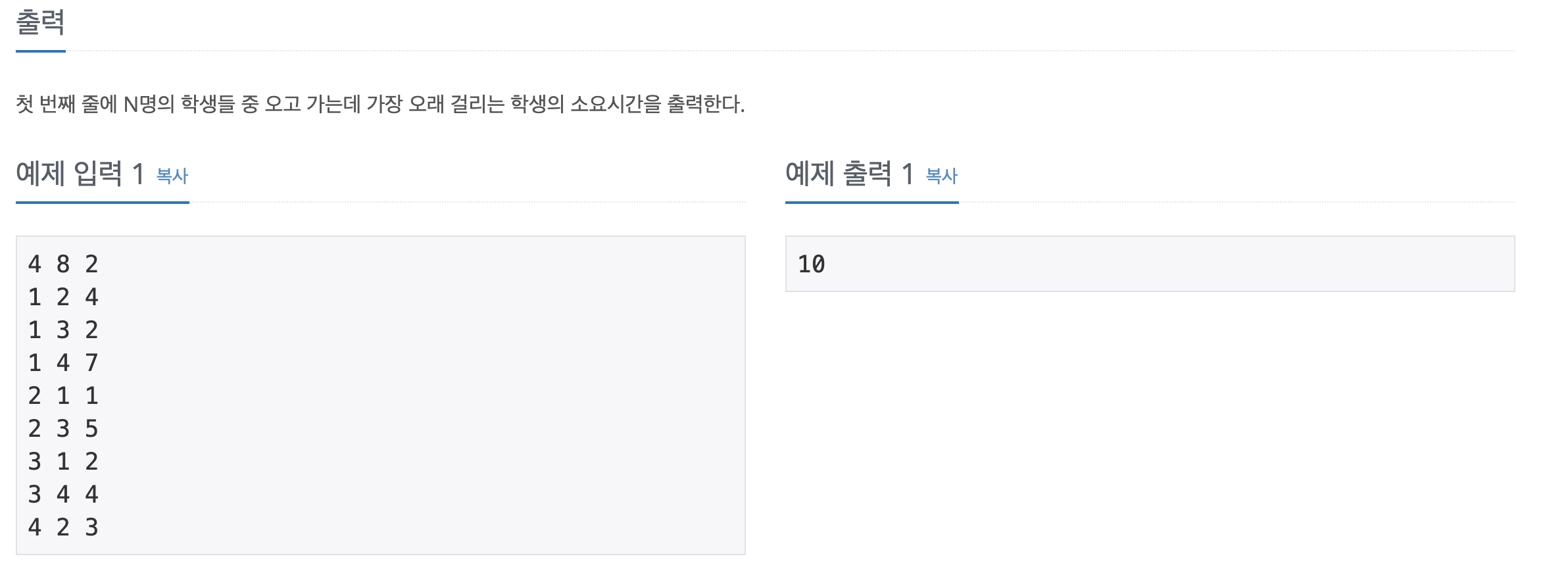
첫째 줄에 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000), M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), X가 공백으로 구분되어 입력된다. 두 번째 줄부터 M+1번째 줄까지 i번째 도로의 시작점, 끝점, 그리고 이 도로를 지나는데 필요한 소요시간 Ti가 들어
www.acmicpc.net
- 풀이
X번 마을을 제외한 모든 마을에 있는 사람이 X번 마을에 방문한 뒤 돌아가는 마을 중 최대값을 출력하면 되는 문제입니다. (단, 모든 마을의 사람은 최단거리로 움직입니다.)
처음 문제를 읽고 플로이드와샬을 통해 풀어보려고 했지만 N의 최대값이 1,000이고 시간제한이 1초인 것을 보고 O(N^3)인 플로이드와샬로는 풀지 못한다고 생각하였습니다.
저는 한점을 통해 모든 점으로 가는 최단거리를 찾는 다익스트라 방법을 사용했고 우선순위큐를 사용하는 다익스트라 알고리즘은 O(VlogV)이므로 시간은 충분했습니다. 문제에서 주어지는 입력은 단방향이므로 X마을로 오고, 가는 방법을 구하기위해 a->b로 오는 자료구조 한개, b->a로가는 자료구조 한개를 추가로 사용해서 두번의 다익스트라를 통해 최단거리를 구해주었습니다.
- 코드
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int N,M,X,answer;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SetData();
System.out.println(answer);
}
// 데이터
private static void SetData() throws Exception {
InputReader in = new InputReader(System.in);
answer = 0;
N = in.nextInt();
M = in.nextInt();
X = in.nextInt();
ArrayList<Node>[] array = new ArrayList[N+1];
ArrayList<Node>[] reArray = new ArrayList[N+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
array[i] = new ArrayList<>();
reArray[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < M; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int w = in.nextInt();
array[a].add(new Node(b, w));
reArray[b].add(new Node(a, w));
}
int[] distance = dijkstra(array);
int[] nDistance = dijkstra(reArray);
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
answer = Math.max(answer, distance[i] + nDistance[i]);
}
}
private static int[] dijkstra(ArrayList<Node>[] array) {
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new Node(X, 0));
boolean[] check = new boolean[N + 1];
int[] distance = new int[N + 1];
Arrays.fill(distance, 10000000);
distance[X] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node nowNode = pq.poll();
if (check[nowNode.x]) continue;
check[nowNode.x] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < array[nowNode.x].size(); i++) {
Node node = array[nowNode.x].get(i);
if (check[node.x] || distance[node.x] <= distance[nowNode.x] + node.distance) continue;
distance[node.x] = distance[nowNode.x] + node.distance;
pq.add(new Node(node.x, distance[node.x]));
}
}
return distance;
}
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int x;
int distance;
public Node(int x, int distance) {
this.x = x;
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node node) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.distance - node.distance;
}
}
class InputReader {
private final InputStream stream;
private final byte[] buf = new byte[8192];
private int curChar, snumChars;
public InputReader(InputStream st) {
this.stream = st;
}
public int read() {
if (snumChars == -1)
throw new InputMismatchException();
if (curChar >= snumChars) {
curChar = 0;
try {
snumChars = stream.read(buf);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if (snumChars <= 0)
return -1;
}
return buf[curChar++];
}
public int nextInt() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c)) {
c = read();
}
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-') {
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
int res = 0;
do {
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
} while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public long nextLong() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c)) {
c = read();
}
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-') {
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
long res = 0;
do {
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
} while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public int[] nextIntArray(int n) {
int a[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = nextInt();
}
return a;
}
public String nextLine() {
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c))
c = read();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
do {
res.appendCodePoint(c);
c = read();
} while (!isEndOfLine(c));
return res.toString();
}
public boolean isSpaceChar(int c) {
return c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == '\t' || c == -1;
}
private boolean isEndOfLine(int c) {
return c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == -1;
}
}'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 11779번 : 최소비용 구하기 2 (0) | 2021.10.29 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 4485번 : 녹색 옷 입은 애가 젤다지? (0) | 2021.10.28 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 5427번 : 불 (0) | 2021.10.26 |
| [프로그래머스/JAVA] 위클리 챌린지 12주차(피로도) (0) | 2021.10.25 |
| [BOJ/JAVA] 백준 1167번 : 트리의 지름 (0) | 2021.10.25 |